What skills does a financial software developer need?
June 13th, 2021 by admin
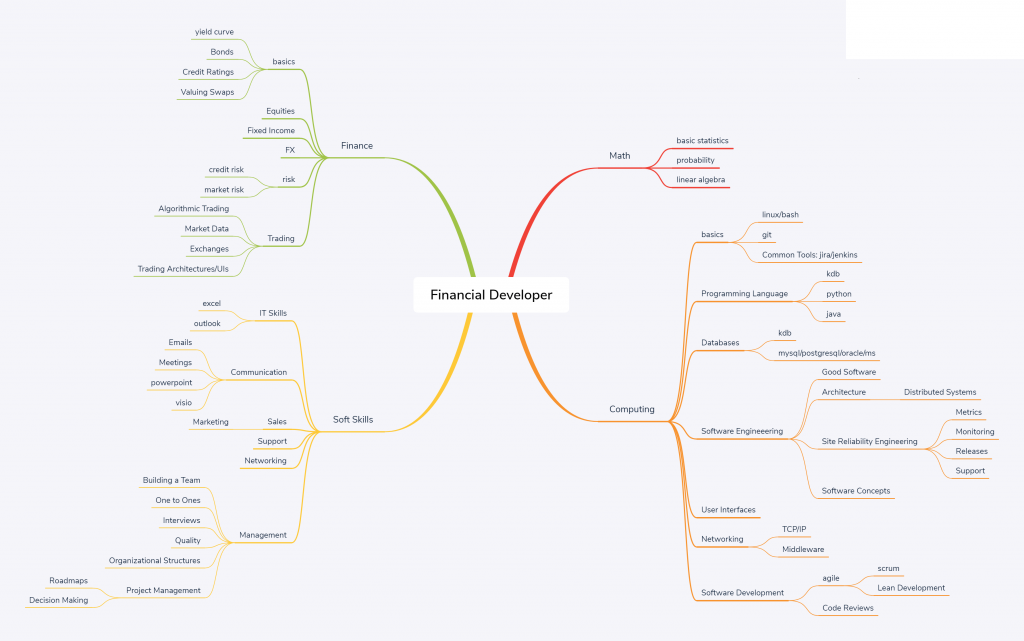
The below network diagram is intended as an outline of the skill set required for a financial software developer.
Note:
- Most individuals should aim to have a strong core. Think of it like a pyramid, where the height is the strength of a skill. Core skills like general computing principles, probability, communication should be built “tall” and very strong. peripheral skills such as python/monitoring will be weaker. An individual will typically only learn 1 or 2 niche areas strongly (T shaped)
- Notice the rough relative sizes of the areas. 55% computing, 10% math, 15% soft skills, 20% finance. This is intended to represent the rough allocation of effort.
- If you only bring 95% techinical skills, you are going to waste time building the wrong thing, build something no one wants or build something useful but no one will know as you haven’t the soft skills to sell it.
- The management branch on the bottom left is optional.
Computing
| Skill | Topic | Sub-Topic | Links | Requirement |
| basics | ||||
| linux | surrey | Change Directories, edit config files, kill processes, copy/move files, check disk space. | ||
| bash | tldp.org | Write a script to periodically sync a directory between servers and schedule it using cron. | ||
| git | git-scm | Checkout, branch, commit, push code. | ||
| Common Tools: jira/jenkins | user-stories | Write a good jira, assign owner. Kick off a build on a common CD platform. | ||
| Programming Language | Knowledge of 2 different programming paradigms. | |||
| kdb | kdb-tree | Write efficient selects for pulling back a subset of data. | ||
| python | Download data from a REST api, calculate average/mean/median for certain metrics. | |||
| java | book | Write a java program to count the number of words in a file. | ||
| Databases | Be aware of the major types of database available and when to use each. | |||
| kdb | kdb-tree | |||
| mysql/postgresql/oracle/ms | Know standard SQL. | |||
| Software Engineeering | peopleware | How to grow good software. | ||
| Good Software | Properties of good software with examples. | |||
| Architecture | Common Enterprise software patterns. | |||
| Distributed Systems | Difficulties with distributed systems and common patterns to solve them. | |||
| Data Processing Pipelines | Common processing Pipeline Patterns | |||
| Site Reliability Engineering | SRE | How reliable should software be? | ||
| Metrics | Ccommon metrics used to measure reliability and when to use each | |||
| Monitoring | What monitoring systems/tools are available? What are monitoring best practices? | |||
| Releases | Accelerate | |||
| Support | Handling outages. Engaging with users. | |||
| Software Concepts | Testing | Testing Methods and knowledge of one test framework | ||
| User Interfaces | dont-think | What makes a good user interface? | ||
| Networking | How computers connect. Expected latency/bandwidth. | |||
| TCP/IP | ports, switches, racks, data centres, windows. | |||
| Middleware | Messaging midddleware: solace/JMS/kafka/MQ. | |||
| Software Development | ||||
| agile | ||||
| scrum | book | Sprints, iterations, standups, restrospectives, story-time. | ||
| Lean Development | lean-startup | When, why and how to develop lean. | ||
| Code Reviews | pragma | Code review best practices. |
Soft Skills
| Skill | Topic | Sub-Topic | Links | Requirement |
| IT Skills | ||||
| excel | Create a table with conditional formatting, calculate sum/average of column, use vlookup | |||
| outlook | Filter emails, create meetings. | |||
| Communication | ||||
| Emails | How to write an email to users, team mates, managers, senior management. | |||
| Meetings | atlassian | What is a meeting meant to accomplish? How to achieve that. | ||
| powerpoint | Prepare a presentation for management. | |||
| visio | Draw an architectural diagram of your system. | |||
| Sales | ||||
| Marketing | Traction | How to get your software used and appreciate by more users. | ||
| Support | ||||
| Networking | Building a network to get things done. | |||
| Management | Grove | |||
| Building a Team | Dysfunctions | |||
| One to Ones | What makes a good one-to-one | |||
| Interviews | How to evaluate cnadidates effectively. | |||
| Quality | How to ensure quality of product. | |||
| Organizational Structures | phoenix | Different structures for management. | ||
| Project Management | ||||
| Roadmaps | ||||
| Decision Making | Which approach to decision making to use when. |